Sep 12, 2022Figure 4.5.1: (a) A particle is moving in a circle at a constant speed, with position and velocity vectors at times t and t + Δt. (b) Velocity vectors forming a triangle. The two triangles in the figure are similar. The vector Δ→v points toward the center of the circle in the limit Δt → 0.
Physics Complete: Circular Motion part two
The object is accelerating even though it is moving at a constant speed. The acceleration is due to the changing velocity vector. The magnitude of the acceleration required to maintain the uniform circular motion is given by, a c= v2 r. The equations of motion for uniform circular motion are: a x (t) = −ω 2rcosωt a y (t) = −ω 2rsinωt v x

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
In uniform circular motion, the net force is perpendicular to the velocity and changes the direction of the velocity but not the speed. If a projectile is launched horizontally, the net force (ignoring air resistance) is perpendicular to the initial velocity, and yet the projectile gains speed as it falls.

Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
IIT JEE and NEET Physics: Motion in One Dimension Problems with Solutions Nine
Dec 14, 2023uniform circular motion, motion of a particle moving at a constant speed on a circle.In the Figure, the velocity vector v of the particle is constant in magnitude, but it changes in direction by an amount Δv while the particle moves from position B to position C, and the radius R of the circle sweeps out the angle ΔΘ. Because OB and OC are perpendicular to the velocity vectors, the

Source Image: studocu.com
Download Image
In Uniform Circular Motion Which Of The Following Are Constant
Dec 14, 2023uniform circular motion, motion of a particle moving at a constant speed on a circle.In the Figure, the velocity vector v of the particle is constant in magnitude, but it changes in direction by an amount Δv while the particle moves from position B to position C, and the radius R of the circle sweeps out the angle ΔΘ. Because OB and OC are perpendicular to the velocity vectors, the
Uniform circular motion Google Classroom An object is undergoing a circular motion. What happens to the velocity of an object moving in a circular path? Choose 1 answer: It remains constant throughout the motion. A It remains constant throughout the motion. It becomes zero at certain points during the motion. B
Short Notes force and motion 1 – d t v = If d is distance, v is speed If d is displacement, v is – Studocu
Evaluate centripetal and tangential acceleration in nonuniform circular motion, and find the total acceleration vector. Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion.
Solved Example 1: Constant speed circular motion or uniform | Chegg.com

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Solved Which of the following quantities are constant for an | Chegg.com
Evaluate centripetal and tangential acceleration in nonuniform circular motion, and find the total acceleration vector. Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion.
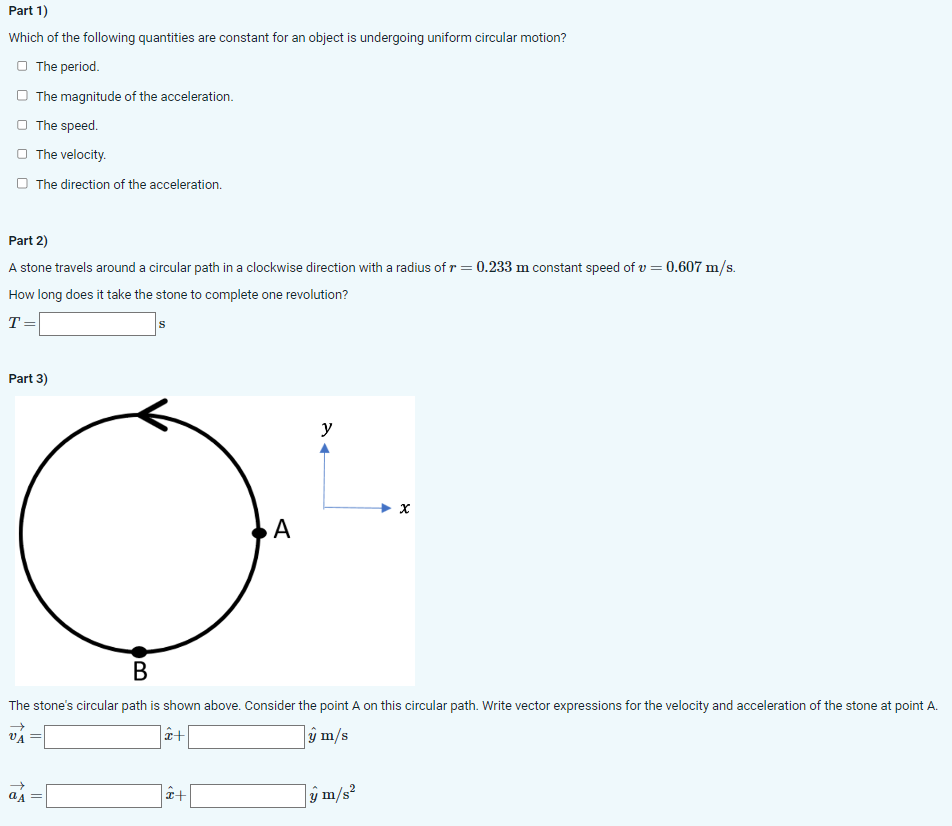
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Physics Complete: Circular Motion part two
In uniform circular motion, the net force is perpendicular to the velocity and changes the direction of the velocity but not the speed. If a projectile is launched horizontally, the net force (ignoring air resistance) is perpendicular to the initial velocity, and yet the projectile gains speed as it falls.

Source Image: physicspractice.blogspot.com
Download Image
IIT JEE and NEET Physics: Motion in One Dimension Problems with Solutions Nine
Sep 12, 2022Figure 4.5.1: (a) A particle is moving in a circle at a constant speed, with position and velocity vectors at times t and t + Δt. (b) Velocity vectors forming a triangle. The two triangles in the figure are similar. The vector Δ→v points toward the center of the circle in the limit Δt → 0.

Source Image: venkatsacademy.com
Download Image
Frank Chapter 1.2 Uniform Circular Motion ICSE Solutions Class 10 Physics
Summary. Uniform circular motion is motion in a circle at constant speed. Centripetal acceleration →a C a → C is the acceleration a particle must have to follow a circular path. Centripetal acceleration always points toward the center of rotation and has magnitude aC = v2/r. a C = v 2 / r.

Source Image: icserankers.com
Download Image
What remains constant in uniform circular motion? – Quora
Dec 14, 2023uniform circular motion, motion of a particle moving at a constant speed on a circle.In the Figure, the velocity vector v of the particle is constant in magnitude, but it changes in direction by an amount Δv while the particle moves from position B to position C, and the radius R of the circle sweeps out the angle ΔΘ. Because OB and OC are perpendicular to the velocity vectors, the
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Physics Class 9 10 CENTRIPETAL FORCE & CENTRIPETAL FORCE Ch 7 CIRCULARM… | Centripetal force, Physics, Gravitation
Uniform circular motion Google Classroom An object is undergoing a circular motion. What happens to the velocity of an object moving in a circular path? Choose 1 answer: It remains constant throughout the motion. A It remains constant throughout the motion. It becomes zero at certain points during the motion. B

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Solved Which of the following quantities are constant for an | Chegg.com
Physics Class 9 10 CENTRIPETAL FORCE & CENTRIPETAL FORCE Ch 7 CIRCULARM… | Centripetal force, Physics, Gravitation
The object is accelerating even though it is moving at a constant speed. The acceleration is due to the changing velocity vector. The magnitude of the acceleration required to maintain the uniform circular motion is given by, a c= v2 r. The equations of motion for uniform circular motion are: a x (t) = −ω 2rcosωt a y (t) = −ω 2rsinωt v x
IIT JEE and NEET Physics: Motion in One Dimension Problems with Solutions Nine What remains constant in uniform circular motion? – Quora
Summary. Uniform circular motion is motion in a circle at constant speed. Centripetal acceleration →a C a → C is the acceleration a particle must have to follow a circular path. Centripetal acceleration always points toward the center of rotation and has magnitude aC = v2/r. a C = v 2 / r.