Exercise 4.10.1 4.10. 1. Determine the partial charges that will give the largest possible bond dipoles. Answer. 4.10: Polar Molecules is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. The molecular polarity of a diatomic molecule is determined by the bond polarity.
Solved Label all polar covalent bonds in the molecule below, | Chegg.com
Identify the compound with the pure covalent bond. O2 O2 has a pure covalent bond because the atoms it contains are identical and thus the electrons in this bond are shared equally. In a polar covalent bond, the atom that attracts the electrons less strongly has: … Select all that apply.

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
Polar bonds are the dividing line between pure covalent bonding and pure ionic bonding.Pure covalent bonds (nonpolar covalent bonds) share electron pairs equally between atoms. Technically, nonpolar bonding only occurs when the atoms are identical to each other (e.g., H 2 gas), but chemists consider any bond between atoms with a difference in electronegativity less than 0.4 to be a nonpolar

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Molecule having non-polar as well as polar bonds but the molecule as a whole is polar : (a) S_2 F… – YouTube 1) is called a nonpolar covalent bond. Figure 4.4.1 4.4. 1 Polar versus Nonpolar Covalent Bonds. (a) The electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared by both hydrogen atoms. This is a nonpolar covalent bond. (b) The fluorine atom attracts the electrons in the bond more than the hydrogen atom does, leading to an imbalance in the electron
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Select The Polar Bonds In The Compounds Below
1) is called a nonpolar covalent bond. Figure 4.4.1 4.4. 1 Polar versus Nonpolar Covalent Bonds. (a) The electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared by both hydrogen atoms. This is a nonpolar covalent bond. (b) The fluorine atom attracts the electrons in the bond more than the hydrogen atom does, leading to an imbalance in the electron Identify the compound below that has a polar bond but is non-polar. Skip to main content. General Chemistry. Start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list. Create Account Sign in. My Course; Learn; Exam Prep; Explore; Bookmarks; Table of contents. 1.
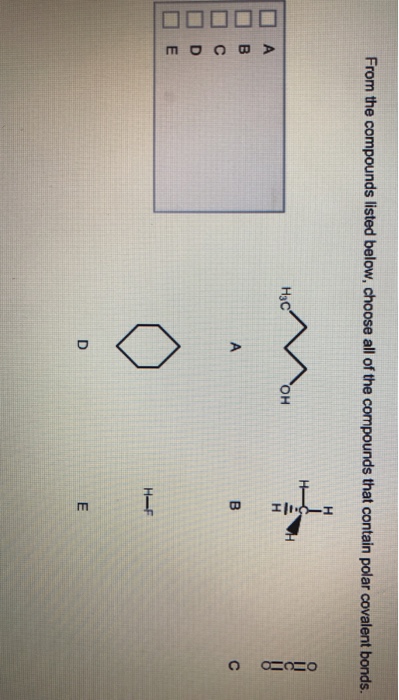
Solved From the compounds listed below, choose all of the | Chegg.com
Science Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Select the polar bonds in the compounds below. Select only bonds. a) CH3Cl b) H2O This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Question: Select the polar bonds in the compounds below. Select only bonds. Solved e skill 1.15 For each of the following compounds, | Chegg.com
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
1,455 Bond Angle Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock Science Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Select the polar bonds in the compounds below. Select only bonds. a) CH3Cl b) H2O This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Question: Select the polar bonds in the compounds below. Select only bonds.

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Solved Label all polar covalent bonds in the molecule below, | Chegg.com Exercise 4.10.1 4.10. 1. Determine the partial charges that will give the largest possible bond dipoles. Answer. 4.10: Polar Molecules is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. The molecular polarity of a diatomic molecule is determined by the bond polarity.

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Molecule having non-polar as well as polar bonds but the molecule as a whole is polar : (a) S_2 F… – YouTube Polar bonds are the dividing line between pure covalent bonding and pure ionic bonding.Pure covalent bonds (nonpolar covalent bonds) share electron pairs equally between atoms. Technically, nonpolar bonding only occurs when the atoms are identical to each other (e.g., H 2 gas), but chemists consider any bond between atoms with a difference in electronegativity less than 0.4 to be a nonpolar

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
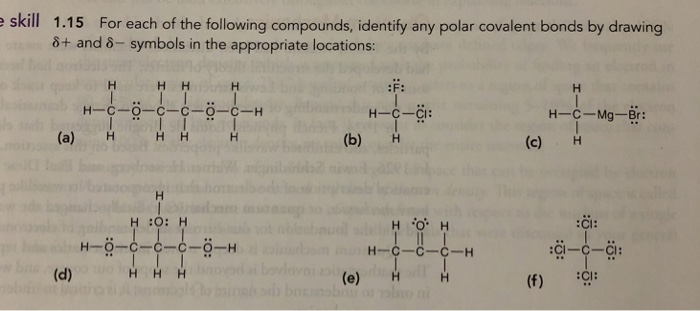
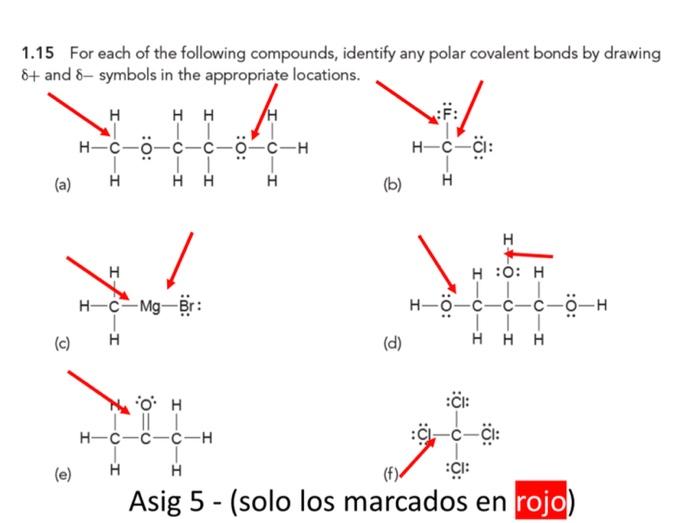
Solved 1.15 For each of the following compounds, identify | Chegg.com An explanation of the polar covalent bond in some compounds is given below. 1. Water (H 2 O) Water is a polar solvent. A polar covalent bond is created when the oxygen (O) atom, more electronegative than hydrogen, pulls the shared electrons towards itself. As a result, the oxygen atom has a partial negative charge associated with it.
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
SOLUTION: Bond polarity and dipole moment of molecules worksheet – Studypool 1) is called a nonpolar covalent bond. Figure 4.4.1 4.4. 1 Polar versus Nonpolar Covalent Bonds. (a) The electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared by both hydrogen atoms. This is a nonpolar covalent bond. (b) The fluorine atom attracts the electrons in the bond more than the hydrogen atom does, leading to an imbalance in the electron

Source Image: studypool.com
Download Image
HYBRIDIZATION AND BONDING Power Points & Bonding Short Answer Questions (64 PGS) | Teaching Resources Identify the compound below that has a polar bond but is non-polar. Skip to main content. General Chemistry. Start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list. Create Account Sign in. My Course; Learn; Exam Prep; Explore; Bookmarks; Table of contents. 1.

Source Image: tes.com
Download Image
1,455 Bond Angle Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock
HYBRIDIZATION AND BONDING Power Points & Bonding Short Answer Questions (64 PGS) | Teaching Resources Identify the compound with the pure covalent bond. O2 O2 has a pure covalent bond because the atoms it contains are identical and thus the electrons in this bond are shared equally. In a polar covalent bond, the atom that attracts the electrons less strongly has: … Select all that apply.
Molecule having non-polar as well as polar bonds but the molecule as a whole is polar : (a) S_2 F… – YouTube SOLUTION: Bond polarity and dipole moment of molecules worksheet – Studypool An explanation of the polar covalent bond in some compounds is given below. 1. Water (H 2 O) Water is a polar solvent. A polar covalent bond is created when the oxygen (O) atom, more electronegative than hydrogen, pulls the shared electrons towards itself. As a result, the oxygen atom has a partial negative charge associated with it.